Subtopic 4: Energy Storage
高能量密度而價格低廉的液流電池鋅 - 碘溴液流電池 (ZIBB)
High-energy-density and low-cost zinc/iodine-bromide redox flow battery (ZIBB)
 |
 |
 |
|
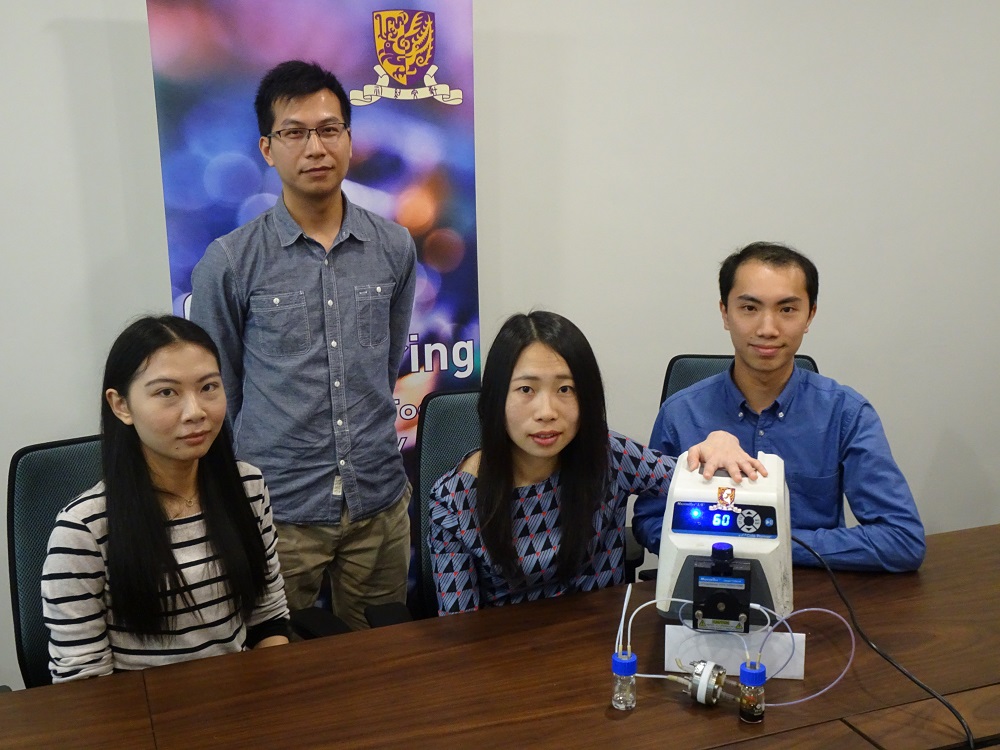
(左起)中大機械與自動化工程學系博士研究生李喆珺小姐、副研究員翁國明博士、盧怡君教授,以及研究助理譚朗彥先生。Members of the research team from CUHK Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering, CUHK. (From left) Ms. Zhejun Li, PhD student; Dr. Guo-Ming Weng, Research Associate; Prof. Yi-Chun Lu, and Mr. Simon Long-yin Tam, Research Assistant. |
鋅-碘溴液流電池設計原型的外觀。The zinc/iodine-bromide redox flow battery prototype. |
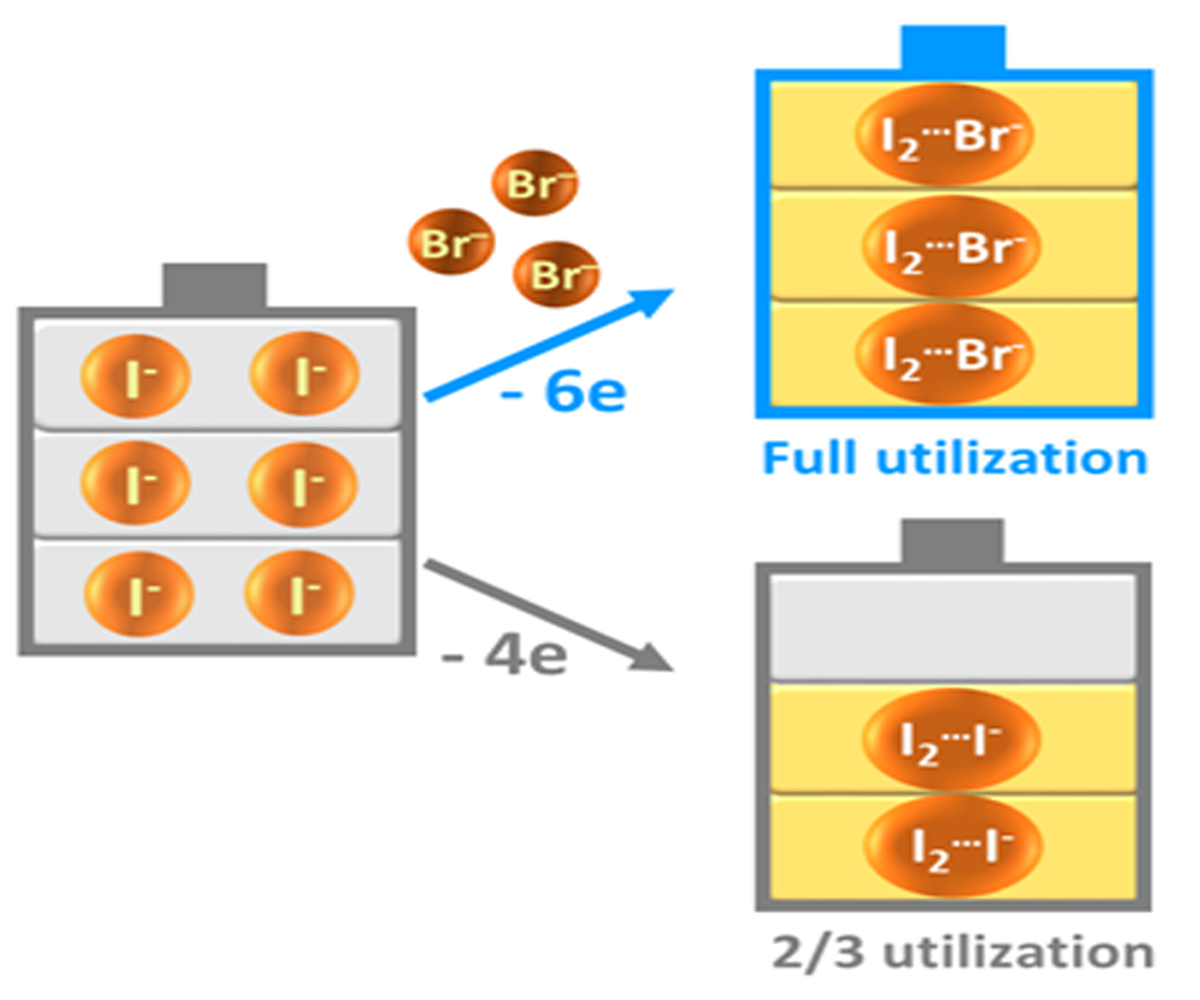
在充電過程中,溴離子(Br-)取代碘三負離子中的碘離子(I-)形成碘溴離子,從而釋放了該部分碘離子以增加儲能容量。During the charging process, bromide (Br-) replaces iodide as the complexing agent to form iodine bromide ions, releasing the iodide (I-) to contribute energy capacity. |
項目說明Project Description
在本港,為電動車補給的公共充電車位數量遠遠趕不上車輛增幅。如能提高電動車電池的儲能容量,充電站的負荷將大大降低。科學家已不斷在儲能技術,尤其是電化學研究方向尋求突破。
In Hong Kong, the number of charging stations lags far behind the growth of electric vehicles they are supposed to serve. Increasing the energy capacity in electric car batteries would considerably relieve the burden for charging stations. Scientists have been making efforts in advancing the energy storage technology, especially on the electrochemical front.
香港中文大學(中大)機械與自動化工程學系助理教授盧怡君教授及其科研團隊最近研發了一種高能量新型鋅-碘溴液流電池,刷新了目前水系液流電池能量密度的紀錄 (101 Wh L-1)。這項突破性的成果近日在國際知名學術期刊《能源及環境科學》(Energy & Environmental Science)發表,並獲英國皇家化學會旗下雜誌《化學世界》(Chemistry World)重點報導。
A high-energy-density zinc/iodine-bromide redox flow battery (ZIBB) has been developed by Prof. Yi-Chun Lu, of the Department of Mechanical and Automation Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong and her research team. ZIBB achieved the highest reported energy density (101 Wh L-1,) for aqueous redox flow batteries to-date. The breakthrough was published in the renowned journal Energy & Environmental Sciencein early 2017, and was recently featured by the magazine Chemistry World, published by The Royal Society of Chemistry, United Kingdom.
溴離子(Br-)的秘密:體積更小,容量更大
The Secret of Bromide Ions (Br-): Less Volume yet More Capacity
鋅-碘液流電池以高溶解度的碘化鋅為主要的活性電解液原料,碘離子(I-)和鋅(Zn)分別為正極與負極的電化學活性物質。在傳統的設計中,電池的高循環壽命得以穩定維持(經五十圈充放電循環後,電池容量保持率高達95%),是由於在充電的電化學反應中,有三分之一的碘離子(I-)充當了碘二離子(I2)的穩定劑,與之結合成為碘三負離子(I3-)。然而,這些充當穩定劑而失去自由的碘離子(I-)在提升電池容量方面的功能被白白浪費。
新研發的鋅-碘溴液流電池破天荒在碘溶液中添加溴離子(Br-)來充當碘離子(I-)的「替身」。溴離子(Br-)與碘二離子(I2)結合成為碘溴離子(I2Br-),同樣可發揮穩定循環性的作用,而被釋放的碘離子(I-)則可增加電池容量。
In zinc/iodine RFB, highly soluble zine iodide is the major active material in the electrolyte, with iodide ions (I-) and zinc (Zn) being the electrochemical active ingredients at the positive and negative electrodes, respectively. In the traditional design, the high and stable cycle life (efficiency as high as 95% over 50 cycles) of the battery was ensured by allowing one-third of the iodide ions (I-) acting as a complexing agent to stabilize the iodine (I2), forming triiodide ions (I3-). However, the power of the iodide ions (I-) in contributing to battery capacity is wasted as they are ‘trapped’ as a stabilizing agent.
The team therefore introduced bromide ions as a replacement for the ‘trapped’ iodide ions (I-), i.e., forming iodine bromide ions (I2Br-) by reacting bromide ions (Br-) with iodine (I2). The process still allows for a stable cycle life in the battery, without sacrificing energy capacity.
潛在應用領域 Potential applications
Electric vehicles
Large-scale energy storage system
可授權專利 Available Patent
Name of Patent: "High-Energy-Density and Low-Cost Flow Electrochemical Devices"
相關文獻 Related Papers:
- Guo-Ming Weng, Zhejun Li, Guangtao Cong, Yucun Zhou & Yi-Chun Lu*. (2017). Unlocking the capacity of iodide for high-energy-density zinc/polyiodide and lithium/polyiodide redox flow batteries. Energy & Environmental Science, 10(3): 735 - 41 [Link]
 |
|
| Project Leaflet 研究計劃簡介 | Available Patent 可授權專利 |
Related news articles:
 |
CUHK Sustainable Campus 續綠中大 (Issue 17) [July 2017] |
|
 |
CUHK Press Release 香港中文大學新聞稿 [12 Apr 2017] Related news articles: |
|
 |
Chemistry World, Royal Society of Chemistry [10 March 2017] |
|
 |
X-MOL [5 Mar 2017] |
|
Copyright © 2014 Faculty of Engineering, The Chinese University of Hong Kong. All rights reserved.
